- Resources
- Cultivating climate-smart dairy: A supplier engagement guide to manure management technologies
Resources
Cultivating climate-smart dairy: A supplier engagement guide to manure management technologies
Published: June 27, 2024 by EDF Staff
For food and agriculture companies engaging with farmers, public and private programs supporting manure management create an opportunity for collaborative investment. They also present a strategic opportunity to address a major source of supply chain emissions: Manure management is responsible for nearly 25% of dairy milk supply chain emissions on U.S. dairy farms.
To help companies sort through the various programs and simplify this process for their suppliers, Environmental Defense Fund created a new actionable guide that covers:
- How to get started with manure management incentive programs
- What management systems exist today and how they fit different operations

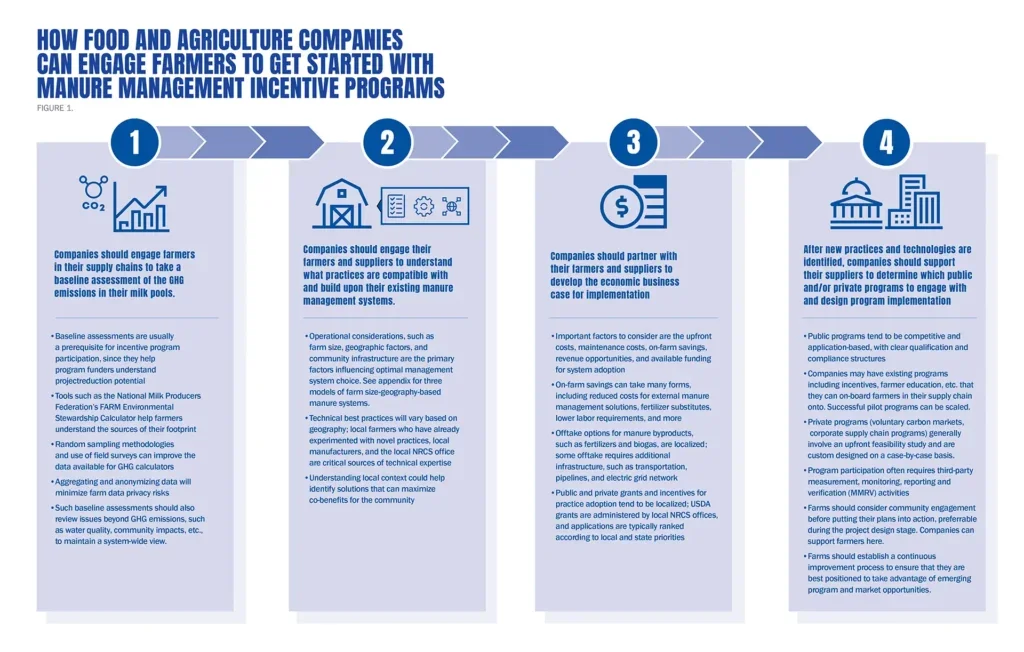
How food and agriculture companies can engage farmers
Companies should:
- Engage farmers in their supply chains to take a baseline assessment of the GHG emissions in their milk pools.
- Engage their farmers and suppliers to understand what practices are compatible with and build upon their existing manure management systems.
- Partner with their farmers and suppliers to develop the economic business case for implementation.
- After new practices and technologies are identified, support their suppliers to determine which public and/or private programs to engage with and design program implementation.
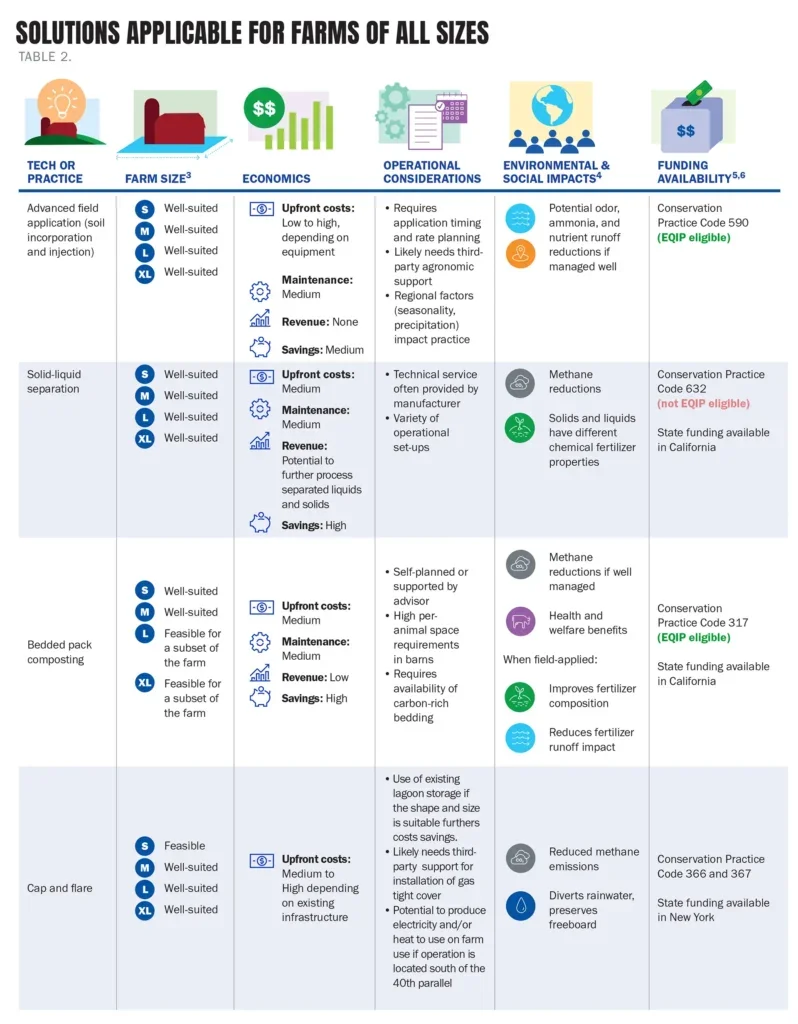
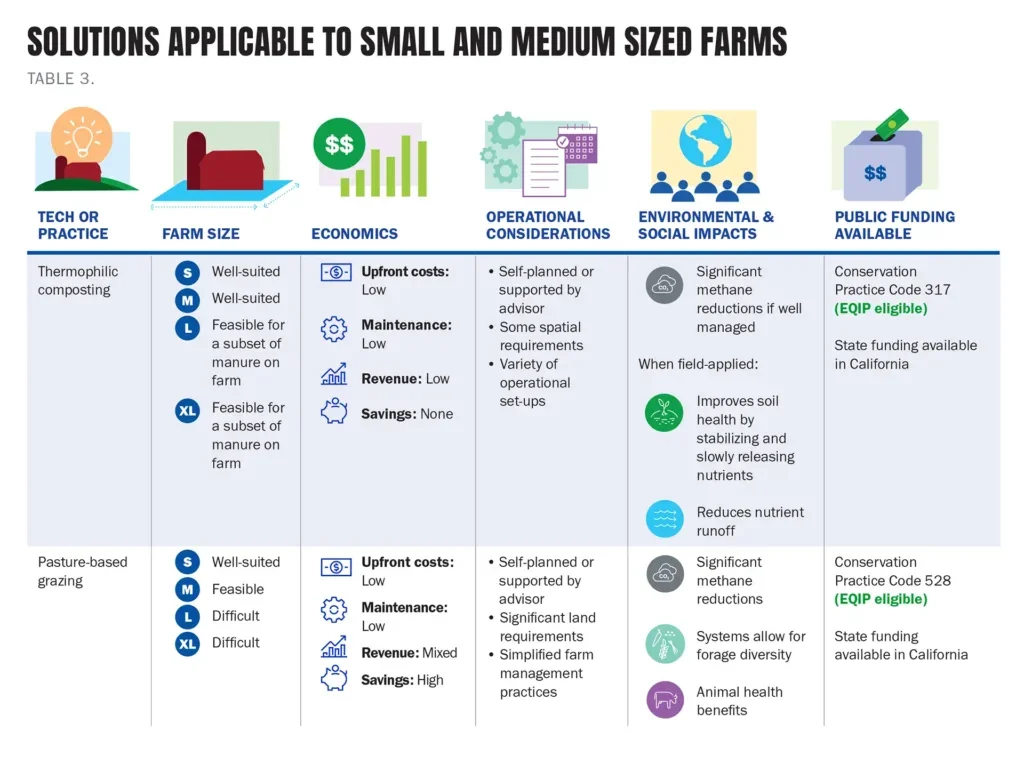
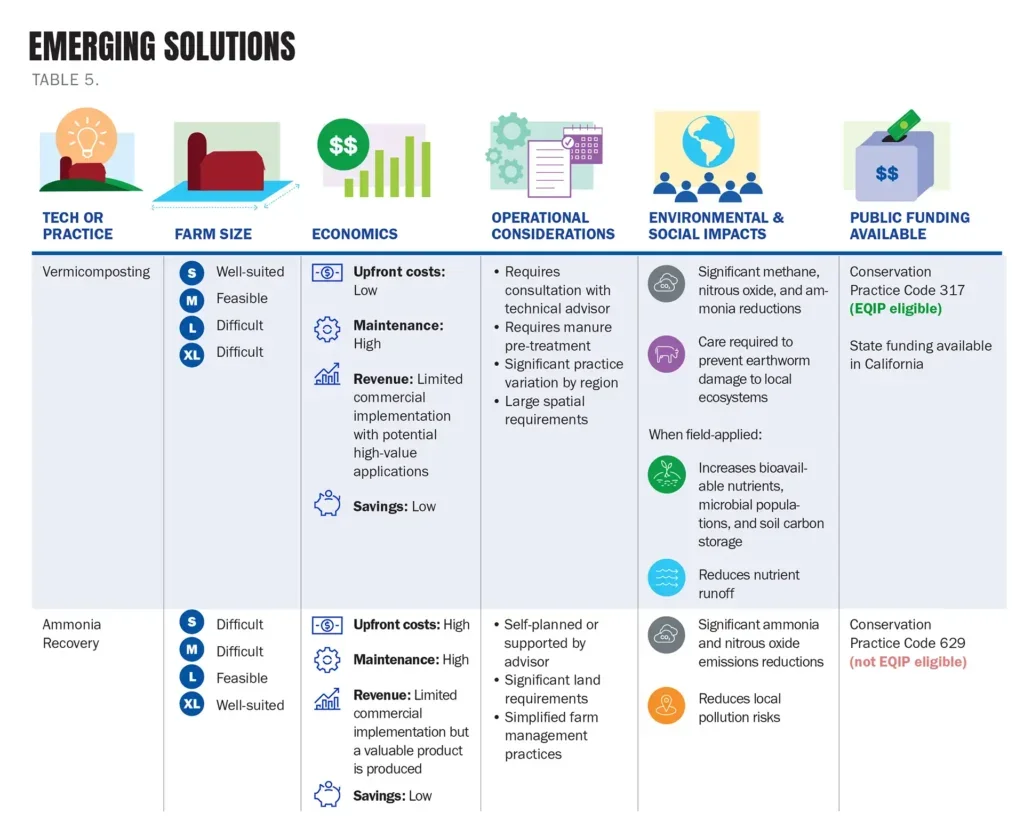
Optimal manure management systems for various operations
Factors such as size, existing on-farm infrastructure, community infrastructure, and geography will impact what management system is optimal for a given farm.
Herd size is often the most significant determinant of what system to adopt, since it drives farm finances, spatial constraints, and the volume of manure that needs to be managed. Geographic factors such as temperature and precipitation will impact the operations of different systems. And finally, funding, offtake opportunities, and equipment options will depend on local availability.
In addition to the factors mentioned above, local pollution concerns, trade-offs, and existing synergies should be considered when evaluating manure management technologies.
In this guide, we explore and consider these factors for solutions applicable on farms of various sizes.
Below, find our summaries of the various factors to weigh when selecting existing and emerging solutions for farms of various sizes.

Cultivating climate-smart dairy: A supplier engagement guide to manure management technologies
Manure management is a powerful tool to mitigate methane emissions from dairy production. In Environmental Defense Fund’s new guide for food companies engaging their farmers on dairy methane solutions, we walk through how to get started with new manure management systems, what manure management systems exist today, and how those systems fit different operations.


-
Dairy Methane Action AllianceView page
-
Good manure management must involve ammonia emissions, tooView resource
-
Strategic Roadmaps for SBTi Forest, Land, & Agriculture TargetsView resource
-
Why food companies must act now to protect public funding for climate-smart agricultureView resource


